
physician, MD, MPA
Despite increasing longevity, aging is an inevitable aspect of life. This issue has been studied for a long time, but the mechanisms of such changes are not fully known. The boundary between normal and pathologic aging is blurred, as all adults experience physiologic and cognitive changes.
When does aging begin?
Different parts of the brain age at different periods of life. For example, scientists have found that the first changes begin after the age of 20. With the onset of 40 years of age, the volume of the brain decreases, and this process continues at an accelerated rate after 70 years of age.
This is due to destructive changes in brain tissue. The volume of gray matter, the main component of the central nervous system, decreases throughout adulthood. The mechanisms contributing to cell death are still unclear.

Types of brain aging
Brain aging is associated with small vessel damage and certain neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), dementia and Parkinson’s disease.
The term “dementia” is also encountered. This is an extreme degree of cognitive impairment in which a person loses independence and becomes dependent on the help of third parties (family, social workers).
It is customary to distinguish vascular cognitive disorders from neurodegenerative disorders because the prognosis and treatment approaches differ.
Vascular cognitive disorders
Vascular cognitive disorders is a general term describing difficulties with thought processes caused by damage to the brain due to impaired blood flow.

Signs of vascular cognitive impairment are:
- problems with attention and concentration;
- decreased ability to switch between tasks;
- increased time spent on familiar tasks;
- slowed “viscous” thinking;
- memory problems;
- restlessness and agitation;
- sleep disturbances, insomnia;
- depression or apathy.
These symptoms can develop after stroke, diabetes, high blood pressure and excess cholesterol, and smoking.
Neurodegenerative disorders
These include Alzheimer’s disease. Decreased aspects of cognition not related to memory may indicate the early stages of this disease. These include finding the right word, trouble understanding visual images, impaired reasoning or judgment.
As it progresses, symptoms become more serious and include increased confusion and behavioral changes.
In the mild form, a person may appear healthy but have trouble understanding the world around them. What can these be?
- Disturbances in recognizing individual objects (e.g., forgets the word “telephone” but can characterize its function – what is being spoken);
- poor judgment, dictated by the person’s suspiciousness;
- loss of spontaneity and sense of initiative;
- confusing dates or knowledge of current location;
- repetition of questions or forgetting recently learned information;
- problems handling money and paying bills;
- problems in planning or problem solving;
- losing things or misplacing them in odd places;
- mood and personality changes;
- increased anxiety and aggression.

Alzheimer’s disease is often diagnosed at this stage. In later stages, signs are added such as:
- Changes in sleep patterns. For example, more sleep during the day and restlessness at night;
- difficulty performing familiar, multi-step tasks such as getting dressed;
- intermittent problems recognizing family and friends;
- hallucinations, delusions, and paranoia;
- impulsive behavior such as undressing at inappropriate times or places or using vulgar language;
- inappropriate emotional outbursts;
- restlessness, agitation, anxiety, tearfulness, wandering – especially in the evening.
Is it possible to stop aging?
Chronological aging is universal for everyone. However, there are individual differences in the biological process. As a bottom line – there is a way to slow this process.
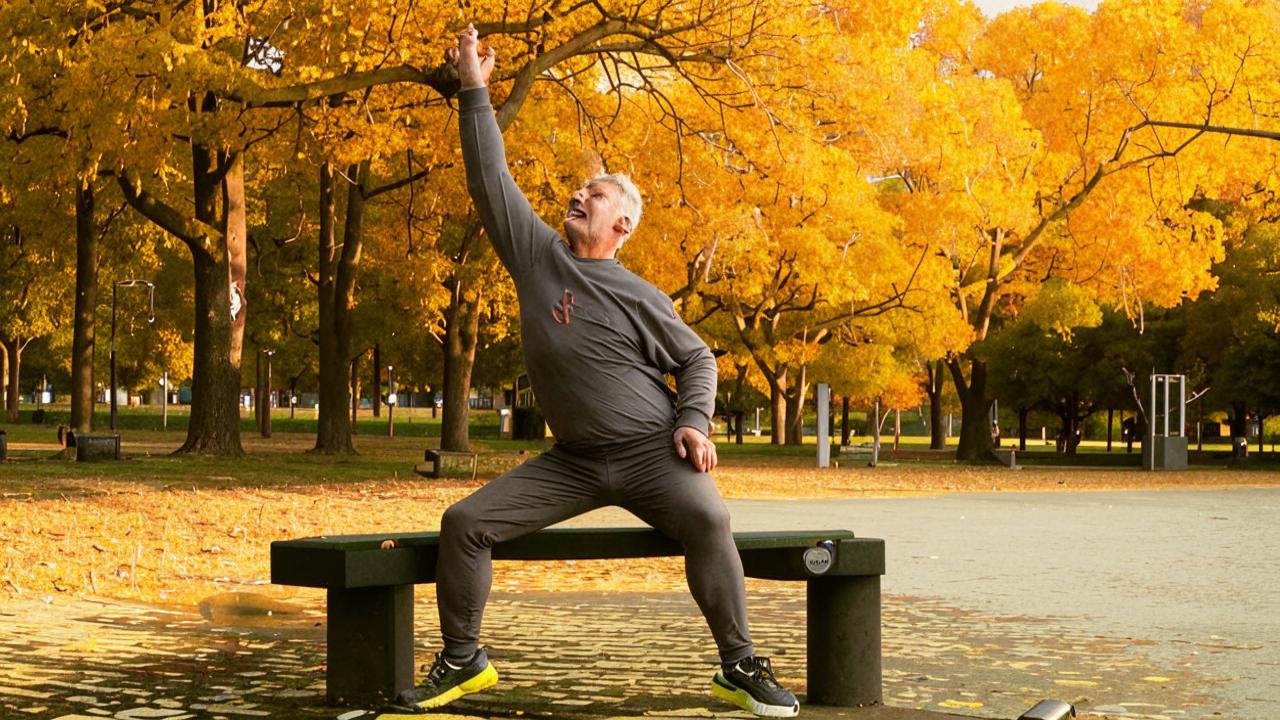

Certain lifestyle changes can play a protective role in age-related cognitive decline. These include exercise, energy restriction and taking antioxidants.
It used to be thought that having a college degree, working as a scientist could shift the onset of dementia. Turns out that’s not true. This only makes it harder to diagnose the early stages. That is, it delays the time to start treatment.
Today, there are known simple and accessible activities that can slow cognitive impairment. These include counting in the mind, doing puzzles and fine motor skills (embroidery, weaving), dancing, solving logic problems, crossword puzzles such as Sudoku.
If any cognitive disorders are suspected, it is not recommended to self-medicate. It is important to consult a specialist – a neurologist, geriatrician (a doctor who treats and prevents diseases in the elderly and old age) or psychiatrist.
Timely initiation of therapy can provide several additional years of independence and personality preservation for a patient with cognitive impairment.





